An echocardiogram is a diagnostic test that uses sound waves to create live images of the heart. These images, known as echocardiograms, allow doctors to monitor the structure and function of the heart. Here are some key points about echocardiograms:
- Purpose: Echocardiograms help assess how well the heart and its valves are functioning. They provide valuable information about heart disease and other heart conditions.
- Procedure: During the test, an ultrasound machine is used to visualize the heart. The sound waves bounce off the heart’s structures, creating detailed images. It’s a non-invasive procedure, meaning you don’t need to stay in the hospital for it.
- What It Shows:
- Heart Structure: Echocardiograms reveal the size and shape of the heart, as well as the chambers, walls, valves, and blood vessels.
- Function: They help evaluate how well the heart pumps blood and identify any abnormalities in wall motion (which can indicate possible heart attacks).
- Types of Echocardiograms:
- Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE): The most common type, where a transducer is placed on the chest to capture images.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE): Involves inserting a probe down the esophagus to get clearer images from behind the heart.
- Stress Echocardiogram: Performed during exercise or medication-induced stress to assess heart function under strain.
Remember, an echocardiogram is a valuable tool for diagnosing and monitoring heart health.
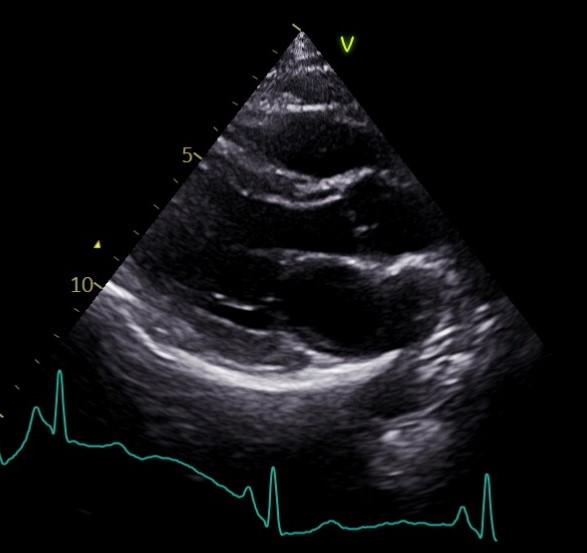
Image – Echocardiogram (Parasternal long axis view)
How long does an echocardiogram take?
The duration of an echocardiogram can vary, but typically it takes around 10 to 20 minutes.
During this time, a trained technician or doctor will use an ultrasound machine to capture images of your heart.
The procedure involves placing a transducer on your chest to visualize the heart’s structures and assess its function.

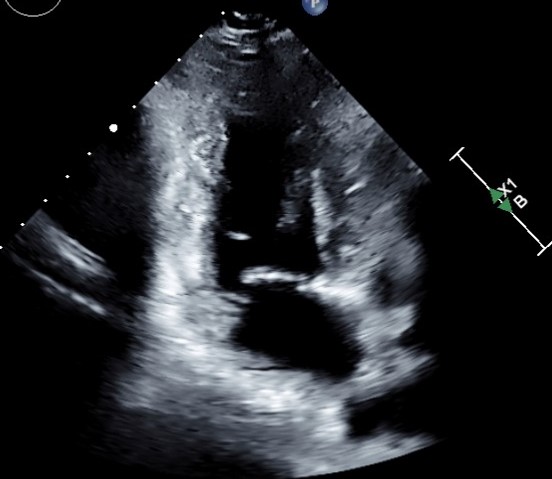

Image- Echocardiogram (various apical views)
What is the procedure of echocardiography?
- Preparation:
- You’ll be asked to lie down on an examination table.
- Electrodes may be placed on your chest to monitor your heart’s electrical activity.
- A trained technician (sonographer) will apply a special gel to your chest.
- Transducer Placement:
- The sonographer will use a handheld device called a transducer.
- The transducer emits high-frequency sound waves that bounce off your heart structures.
- It’s placed on different areas of your chest to capture images from various angles.
- Image Acquisition:
- As the transducer moves, it sends sound waves through your chest.
- These waves penetrate your skin and other tissues, reaching your heart.
- When the waves encounter heart structures, they bounce back (or “echo”) to the transducer.
- The echoes are converted into detailed images of your heart.
- Types of Echocardiograms:
- Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE):
- The most common type.
- The transducer is placed on your chest and moved to capture images.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE):
- Involves inserting a probe down your esophagus.
- Provides clearer images from behind the heart.
- Stress Echocardiogram:
- Performed during exercise or with medication-induced stress.
- Assesses heart function under strain.
- Transthoracic Echocardiogram (TTE):
- Interpretation:
- A cardiologist or doctor analyzes the images.
- They assess heart size, shape, valves, blood flow, and any abnormalities.
- Echocardiograms help diagnose conditions like heart disease, valve disorders, and heart failure.


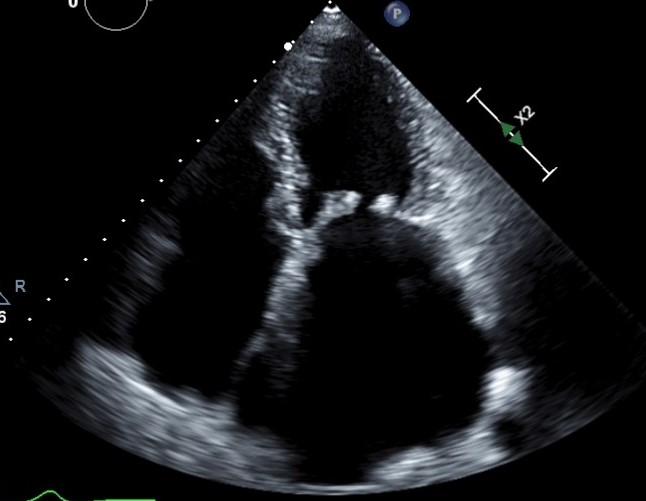


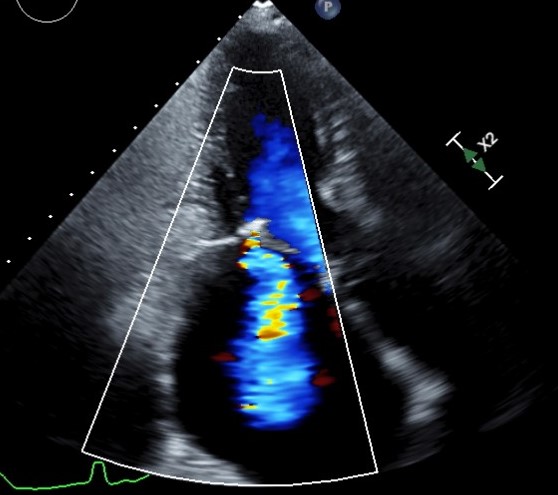
Image- A patient with rheumatic heart disease. Echocardiography helped in diagnosis of valve problems.
What are the risks associated with echocardiography?
Echocardiograms are considered very safe and have minimal risks. Here’s what you need to know:
- External Echocardiogram:
- This type of echocardiogram is noninvasive and does not use radiation.
- Some people may feel uncomfortable lying in one position during the test.
- The risk is low compared to other types of echocardiograms.
- Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE):
- TEE involves inserting a probe down the esophagus for clearer images.
- Risks include:
- Bad reaction to the sedative.
- Sore throat (rarely, minor throat injury).
- Stress Echocardiogram:
- Performed during exercise or with medication-induced stress.
- Minor complications may arise from exercise or medication use.
- General Considerations:
- Risks may vary based on your medical history.
- Discuss any concerns with your doctor before testing.
Pingback: What is transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) test? | Dr. Nitin Parashar